Definition
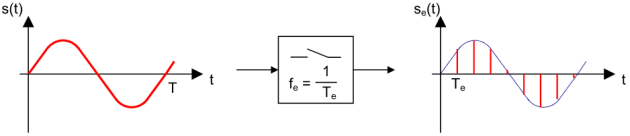
Sampling a continuous signal is the process of capturing discrete samples of the signal at specific intervals (taking instantaneous values at precise times). This results in a discrete signal represented as a sequence of numbers that mirrors the original signal. The purpose of sampling is to facilitate storage, transmission, or processing of the signal.
se(t) = s(n.Te)
With n as an integer and Te representing the sampling period.
A sampler, often represented by a switch in Figure 1, performs this operation.