Change of Scale (Compression / Dilatation) / Scaling
This operation enables the stretching or compression of a signal over time.
y(t) = x(at) with a > 0
Graphically, y(t)=x(at) (with a being the scale factor).
If 0 < a < 1, y(t) is a dilated version of x(t).
If a > 1, y(t) is a compressed version of x(t).
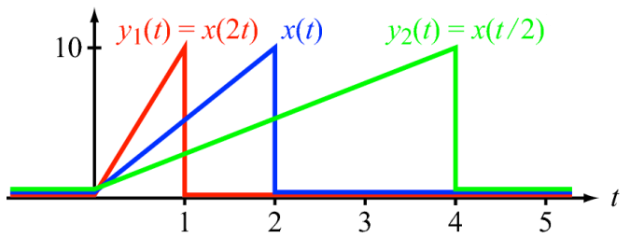
Figure 15 : Example of time scaling.