Causality Observation:
Signal Causality :
A signal is deemed causal if it is zero for any negative time value (i.e., f(t) = 0 for t <0).
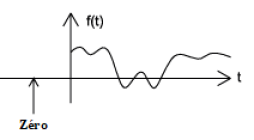
Figure 10: Causal Signal.
Signal Anti-Causal :
An anti-causal signal is characterised by being zero for all positive time values (refer to Figure 11).
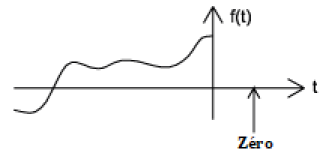
Figure 11: Anti-Causal Signal.
Signal Non-Causal :
Non-causal signals are signals that exhibit both positive and negative non-zero values (refer to Figure 12).
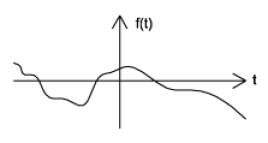
Figure 12: The anti-Causal Signal.
Note : Period, Frequency :
We also refer to periodic signals as signals x with a period of T. A signal is considered periodic if, for any moment t₀, x(t₀ + T) = x(t₀); in other words, the signal repeats itself, identical to itself, after a time interval T.
Its frequency, denoted as f, is defined as f = 1/T.
Frequency is the inverse of time and is expressed in Hertz (Hz).