Random Signals
Definition : Definition
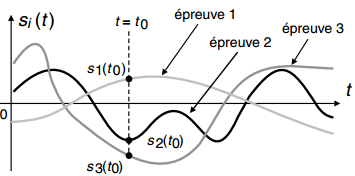
A random signal, also known as a stochastic process, is a signal that does not repeat itself under the same conditions in the experiment that produced it.
It is denoted by X(t,ω) where ω is a variable (random variable) that reflects a random draw. X(t, ωi) represents a realisation of X(t, ω) for a particular draw, ωi.
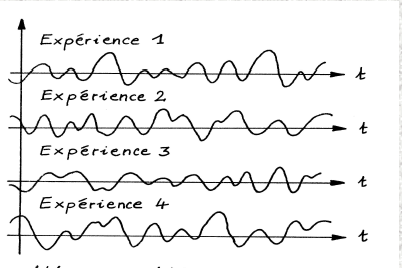
Example :
For example :
the speech signal
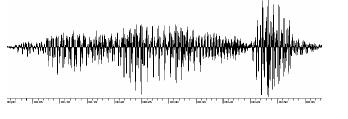
White noise: a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables
A random process describing a random signal is called stationary if the statistical properties (mean, standard deviation, etc.) are independent of the choice of the origin of time.
It is often more practical to conduct a single long-term experiment on a process than to conduct multiple tests of the same process related to the same physical phenomenon. The process is considered ergodic if the averages over multiple realisations are equivalent to the time averages corresponding to a single realisation [10].