Aperçu des sections
-
This course is organized into four parts presenting the theoretical and practical foundations of geographic information systems (GIS).
1. Together theses courses constitute an introduction to GIS and require no prior knowledge.
2. By following this introduction to GIS you will quickly acquire the basic knowledge required to create spatial databases, produce high-quality maps, and cartographic representations.
3. This is a practical course create spatial databases and is based on software, including PostGIS and Oracle Spatial.
4. This is a practical course and is based on software, including MapInfo, QGIS, and ArcGIS.
This course is intended for:
- 2nd year engineering students (Master - IMSI and RT specialty)
- Semester 4
- Computer Systems Engineering Department
Dr. BRAHAMI Menaouer, Associate Professor
Computer Systems Engineering Department
E-mail: menaouer.brahami@enp-oran.dz
-
Geographic Information System (GIS) is an information system capable of organizing and presenting spatially referenced alphanumeric data, as well as producing plans and maps. The term refers to software tools (ArcGIS, Qgis, ...). However, the concept encompasses software, data, hardware, and the know-how related to the use of these.
-
1. Introduction and Objective:
A first practical work aims to present the Mapinfo software, automatic mapping software with GIS functionalities, and its basic functionalities. It contains exercises to put into practice the knowledge acquired by the students. In addition, we present the following educational objectives:
- Make a presentation of data on a map;
- Use simple automated SQL queries to make selections;
- Set up and perform thematic analyses;
- Integrate maps into word processing or layout software;
- Map a file of individuals.
2. Level reached: autonomy to represent their data on a map, distribute their maps.
3. Pedagogy: 15% theory, 85% practice: case study, scenarios.
4. Mode: face-to-face
5. Rhythm: continuous

-
ABOUT: QGIS is a free cross-platform Geographic Information System (GIS) released under the GPL license. It handles many vector and raster geographic data formats, as well as databases. This practical work part allows you to discover all the basic functionalities of the software.
-
-
In particular, you will learn:
1- To characterize spatial objects and/or phenomena (territory modeling) with respect to their position in space (through coordinate systems, projections, and spatial relationships) and according to their intrinsic nature (object/vector mode vs. Image/raster mode);
Example : Digitizing layers (polygon, polyline and point) in ArcGIS
8.4 Mo · Modifié 10 mars 23, 11:10
-
-
-
In particular, you will learn:
1- About the different means used to acquire spatial data; including direct measurement, georeferencing images, digitization, existing data source, etc.);
2- About the different ways in which geodata can be stored - notably, files and relational databases;
14.7 Mo · Modifié 10 mars 23, 11:40 -
The objective of this pratical work is to learn how to register one image in relation to another.
1. Download and Install ArcGIS Pro
2. The official website of the ArcGIS Tool
https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-online/overview
3. Introduction to ArcGIS Pro
-
The ArcGIS Desktop installer allows you to select a pre-determined set of installation features (full installation).
-
-
-
This part aims to understand spatial databases: installation and use of PostGIS and create a spatial database.
-
Purposes of the Pratical Work/Tutorials:
- Know how to implant files;
- Know how to edit imported layers;
- Know how to select objects by attribute;
- Knowing how to map to help with decision-making;
Example - A how-to video: Import Excel data to ArcMap
-
In this example, we show through the website the benefits and positive feedback related to the use of QGIS on practical cases.
-
-
-
The course provides a broad introduction to the methods of representing the real world and the models used for storing geospatial information.
-
Spatial data analysis is an old and vast field that brings together many methodologies, some general and others more specific to a specific thematic field.
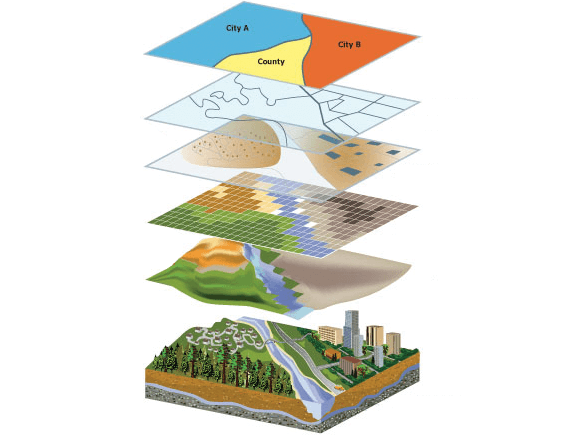
-
This activity is part of the spatial database (Modeling) part.
-
-
-
Coordinate Reference System (CRS) is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific
map projection , as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems. -
Convert Algeria Coordinates in a Single Click:
1. Using ExpertGPS as a Algerian GPS, GIS, and CAD Coordinate Converter.
2. ExpertGPS Converts Between Any of These Algerian Coordinate Formats.
3. ExpertGPS Reprojects Your Data Between Any of These Datums.
-
In this course we extend the knowledge of data management in spatial databases with a focus on spatial data management, usage and analysis. We will introduce spatial indexes, topological data models and spatial queries. Open source software (PostGIS) will be used as an example.
1. How to Create Spatial Databases in PostGIS (PostgreSQL) - Import Shapefile into the Database
2. Import Shapefile to Postgresql ( via QGIS and Postgis Shapefile Import/Export Manager)
-
-
This course treats a specific advanced topic of current research interest in the area of handling spatial, temporal, and spatio‐temporal data.
-
This course will start with defining spatial data science and answering why spatial is special from three different perspectives - business, technology, and data. As well, this course explores the application of spatial data science to uncover hidden patterns, visualization, and improve predictive modeling.
1. Spatial Data Mining - Link Book
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/0-387-25465-x_39
2. Spatial Data Science Overview - Recorded lecture by Luc Anselin at the University of Chicago (October 2016).
3. Spatio-Temporal Data Mining in Encyclopedia of Database Systems. Springer
https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-0-387-39940-9_361
-
This activity is part of the spatial Data Mining part. As well, it falls within the framework of strengthening students' knowledge of the two concepts GIS and Machine/depp learning.
-
-
-
Knowledge of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is an increasingly sought after skill in in the socio-economic sector. This Specialization, you will learn how to use GIS software in a professional setting.
1. Create and work with vector and raster data.
2. Develop and analyze data for the geospatial analysis project.
3. Spatial Database systems and their types

-
I put myself at your disposal a set of reference concerning the concept GIS and visualization.
-
We provide you with the different chapters of the GIS module in the format: Online course material (web).
-